GLASS

Glass is anon-crystalline, frequently transparent unformed solid, that has wide practical, technological, and ornamental use in, for illustration, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most frequently formed by rapid-fire cooling ( quenching) of the molten form; some spectacles similar as stormy glass are naturally being. The most familiar, and historically the oldest, types of cultivated glass are”silicate spectacles” grounded on the chemical emulsion silica (silicon dioxide, or quartz), the primary element of beach. Soda-lime glass, containing around 70 silica, accounts for around 90 of cultivated glass. The term glass, in popular operation, is frequently used to relate only to this type of material, although silica-free spectacles frequently have desirable parcels for operations in ultramodern dispatches technology. Some objects, similar as drinking spectacles and eyeglasses, are so generally made of silicate- grounded glass that they’re simply called by the name of the material. Although brittle, buried silicate glass will survive for veritably long ages if not disturbed, and numerous exemplifications of glass fractions live from early glass- making societies. Archaeological substantiation suggests glass- making dates back to at least BC in Mesopotamia, Egypt, or Syria. The foremost given glass objects were globules, maybe created accidentally during metalworking or the product of faience. Due to its ease of formability into any shape, glass has been traditionally used for vessels, similar as coliseums, vases, bottles, jars and drinking spectacles. In its most solid forms, it has also been used for paperweights and marbles. Glass can be coloured by adding essence mariners or painted and published as enamelled glass. The refractive, reflective and transmission parcels of glass make glass suitable for manufacturing optic lenses, prisms, and optoelectronics accoutrements. Extruded glass fibers have operation as optic fibers in dispatches networks, thermal separating material when matted as glass hair so as to trap air, or in glass- fiber corroborated plastic (fiberglass).
TYPES OF GLASS
There are four types of glass
Annealed Glass
Heat Strengthened Glass
Tempered or Toughened Glass.
Laminated Glass.

Annealed Glass
Annealed glass is also known as pier or clear glass. It’s a kind of glass that isn’t quenched after the heating process; it’s allowed to cool sluggishly. Annealed glass is gently cooled in the‘annealing lehr’where the molten glass is subordinated to a controlled cooling process that helps free it from internal stress. After this is done, annealed glass becomes ready to be cut and worked on. Annealed glass can be used for farther processing to gain tempered glass, laminated glass, toughened glass, etc. Piecemeal from processing, they can be carpeted with a essence oxide to make a tinted glass which is utilised in protection against solar light.
Types
Clear glass- It’s a kind of annealed glass which offers extreme translucency and clarity.
Tinted glass-Tinted glass is annealed glass that has a coating or a film that imparts its colour and reduces its light transmission parcels.
Frosted glass-Frosted glass is a translucent annealed glass made by the process of sandblasting or acid drawing. Its levelled, rough face gives it a foggy appearance.
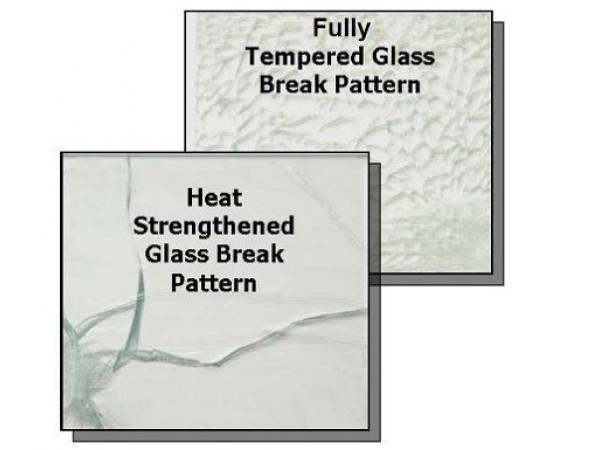
Heat Strengthened Glass
Heat- strengthened glass has been subordinated to a heating and cooling cycle and is generally doubly as strong as annealed glass of the same consistence and configuration.
Heat- strengthened glass has lesser resistance to thermal loads than annealed glass and, when broken, the fractions are generally larger than those of completely tempered glass.
Heat- strengthened glass isn’t a safety glass product as defined by the colourful law associations.
Heat- strengthened glass is intended for general glazing, where fresh strength is asked to repel wind cargo and thermal stress.
Heat- strengthened glass doesn’t bear the strength of completely tempered glass and is intended for operations that don’t specifically bear a safety glass product.
Heat- strengthened glass cannot be cut or drilled after heat- strengthening and any differences, similar as edge grinding, beach firing or acid drawing, can beget unseasonable failure.
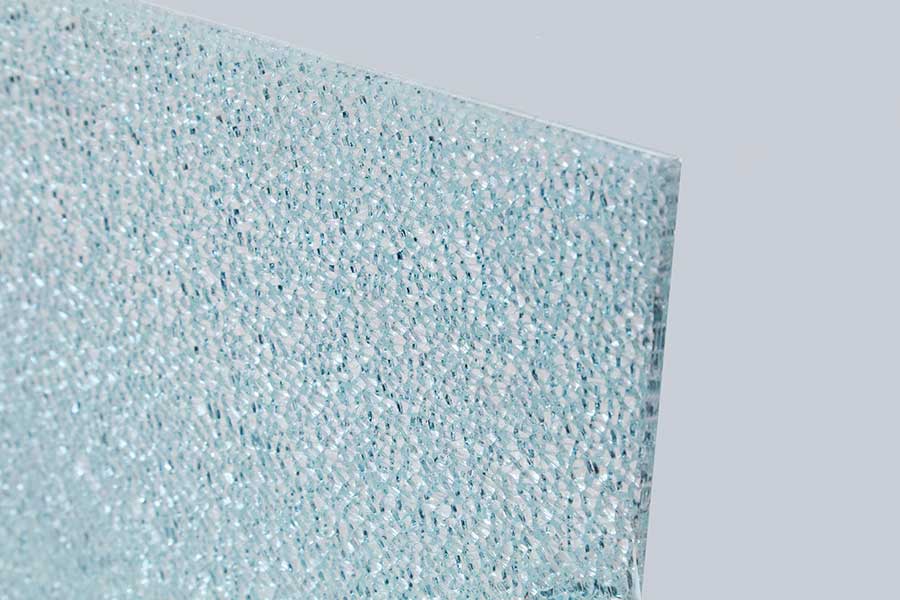

Tempered or Toughened Glass
Toughened or Tempered glass can be a shatterproof style of glass that is processed by controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase strength compared to Normal glass. Toughened puts the outer surfaces into compression and therefore the interior into tension. Such stresses cause the glass, once broken, to crumble into little granular chunks rather than breakage into jagged shards as flat solid does. The granular chunks are less possible to cause injury. As a results of its safety and strength, tempered glass is employed in an exceedingly kind of rigorous applications, as well as rider vehicle windows, shower doors, branch of knowledge glass doors and tables, white goods Trays, mobile screen protectors, as an element of bulletproof glass, for diving masks, and varied varieties of plates and kitchen utensil.
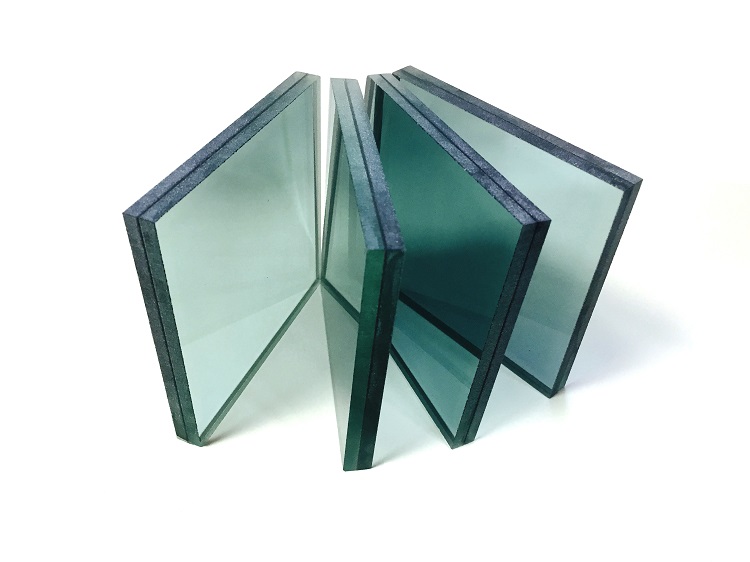

Laminated Glass
Laminated glass (LG) is a type of safety glass that holds together when shattered. In the event of breaking, it’s held in place by a thin polymer interlayer, generally of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), lonoplast polymers, cast in place (CIP) liquid resin, or thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), between its two or further layers of glass. Interlayer, made through heat and pressure, keeps the layers of glass clicked indeed when broken, and its high strength prevents the glass from breaking up into large sharp pieces. This produces a characteristic”spider web” cracking pattern when the impact isn’t enough to fully pierce the glass. The thermoset EVA offers a complete cling (cross-linking) with the material whether it’s glass, polycarbonate, PC, or other types of products. Laminated glass is used for armature, glazing, machine safety, photovoltaic, UV protection, and cultural expression. The most common use of laminated glass is skylight glazing and machine windshields. In geographical areas taking hurricane-resistant construction, laminated glass is frequently used in surface storefronts, curtain walls, and windows. Laminated glass is also used to increase the sound sequestration standing of a window, because it significantly improves sound attenuation compared to monolithic glass panes of the same consistence. For this purpose a special” aural PVB” emulsion is used for the interlayer. In the case of the EVA material, no fresh aural material is needed, since the EVA provides sound sequestration. PU is an elastic material, so sound immersion is natural to its nature. An fresh property of laminated glass for windows is that an acceptable TPU, PVB or EVA interlayer can block nearly all ultraviolet radiation..

